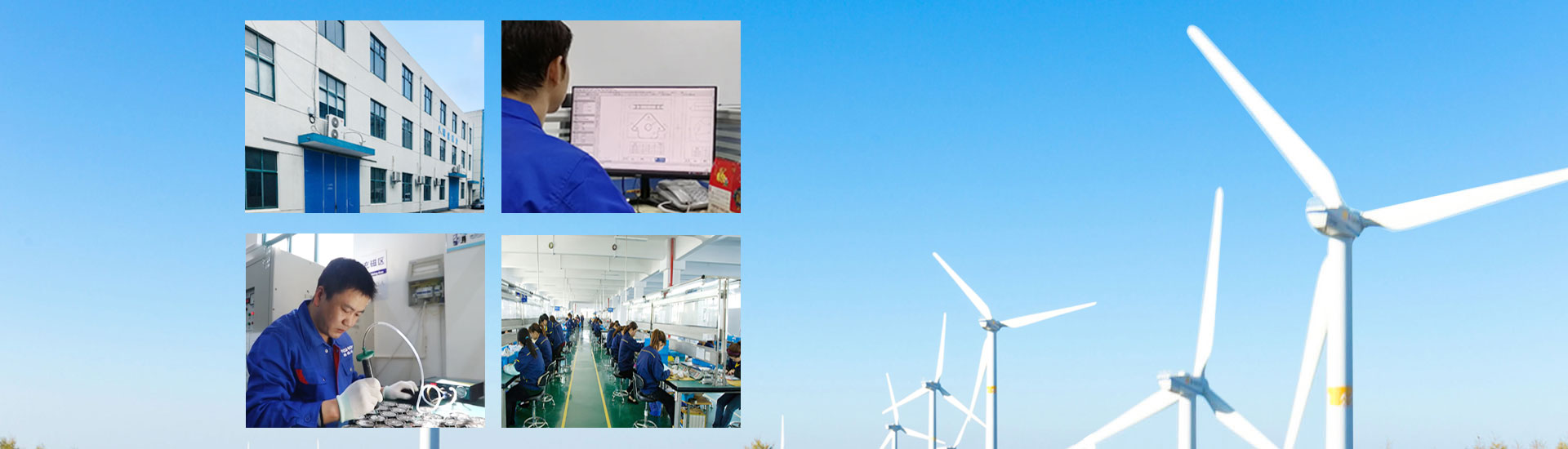
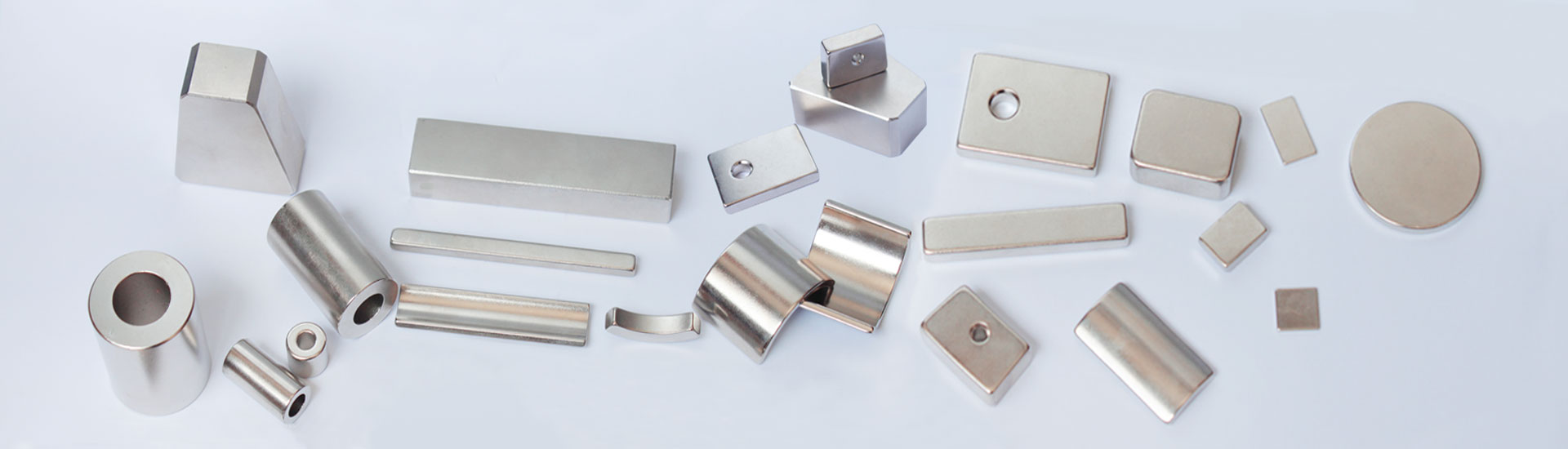
The production of magnets involves several key steps, depending on the type of magnet (e.g., permanent magnets like Neodymium Iron Boron (NdFeB), Ferrite, or Samarium Cobalt (SmCo), or temporary magnets like electromagnets). Below is a general overview of the manufacturing process for sintered NdFeB magnets, the most widely used high-performance permanent magnets:
1) Raw Material Preparation
Ingredients: Neodymium (Nd), Iron (Fe), Boron (B), and trace additives (e.g., Dysprosium (Dy) or Terbium (Tb) for high-temperature stability).
Alloying: The raw materials are melted in a vacuum induction furnace to form an alloy, which is then cooled into ingots or strips via strip casting (rapid solidification for fine microstructure).
2) Powder Production (Jet Milling)
The alloy is crushed into coarse powder and then finely pulverized into micron-sized particles using jet milling (to ensure uniform particle size for optimal magnetic properties).
3) Pressing (Orientation & Compaction)
Magnetic Alignment: The powder is placed in a mold and exposed to a strong magnetic field to align the particles in the preferred direction (anisotropic magnets).
Pressing Methods: Isostatic Pressing (CIP: Cold Isostatic Pressing or HIP: Hot Isostatic Pressing) for uniform density, Die Pressing for simpler shapes.
4) Sintering
The compacted powder is heated in a vacuum or inert gas furnace at 1,000–1,100°C to fuse particles into a solid block (densification).
Heat Treatment: Further annealing improves coercivity (resistance to demagnetization).
5) Machining & Finishing
Sintered magnets are brittle and require diamond-coated tools for:
Cutting (wire EDM, slicing).
Grinding (surface finishing).
Chamfering/Drilling (for specific shapes).
6) Coating (Corrosion Protection)
NdFeB magnets are prone to oxidation and require coatings:
Nickel (Ni) plating (most common).
Epoxy, Zinc, or Gold plating for specialized environments.
7) Magnetization
The magnet is exposed to a pulsed magnetic field (≥3 Tesla) to align its domains, activating its full magnetic strength.
8) Quality Testing & Packaging
Tests: Magnetic flux (Gauss meter), coercivity, dimensional accuracy.
Packaging: Anti-rust paper, vacuum sealing for sensitive applications.

 中文
中文